Debunk common summer swimming pool myths for a safer experience. Eating before swimming won't lead to drowning; cramps are from exercise, not food. Sunscreen is vital—water intensifies UV rays. Sunburn won't become a tan; use SPF 25+. Rinse off before swimming to keep water clean—chlorine isn't enough. Ability to float is about technique, not genetics—practicing positioning and relaxation techniques can help. Uncover more myths to maximize your pool enjoyment.
Key Takeaways
- Eating before swimming doesn't cause drowning; cramping is from exercise, not digestion.
- Sunscreen is vital for swimming to prevent sunburn from intensified UV rays.
- Sunburn doesn't turn into a tan; protect skin with SPF 25+ sunscreen.
- Rinsing off before swimming maintains water quality and prevents harmful chemicals.
- Proper technique and body awareness help anyone float in water effortlessly.
Eating Before Swimming Does Not Cause Drowning
Contrary to popular belief, consuming food before swimming does not lead to drowning as commonly misconceived. While some may fear that swimming on a full stomach can result in tragic consequences, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim.
The myth likely originated from concerns about cramping during swimming after eating. However, cramping is primarily caused by vigorous exercise rather than digestion.
It is advisable to wait a short period after consuming a meal before swimming to avoid discomfort due to the weight of food in the stomach. Opting for light snacks or simple carbohydrates before swimming can even help stabilize blood sugar levels, contributing to a safer and more enjoyable swimming experience.
Sunscreen Is Essential for Swimming
Consuming food before swimming does not pose a drowning risk; however, protecting your skin with sunscreen is essential while enjoying time in the water.
- Submerging in water increases the need for sunscreen.
- Water intensifies the sun's harmful UV rays.
- Sunscreen is essential to prevent sunburn while swimming.
- Reflection of the sun's radiation in water doubles the risk of sunburn.
Sunburn Does Not Turn Into a Tan

Skin damaged by sunburn does not naturally evolve into a tan. When skin is exposed to excessive ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, it triggers a protective response in the body. Sunburn occurs as a result of this damage, causing redness, pain, and potential blistering.
Contrary to popular belief, sunburned skin does not shift into a tan. Instead, the body's response involves sending blood to repair the damaged skin cells, which may result in peeling as the body sheds the affected skin.
It is vital to protect the skin from sunburn by using sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 25 or higher, as prolonged sun exposure can lead to severe consequences such as sun poisoning or an increased risk of skin cancer.
Rinsing Off Before Swimming Is Important
Before entering a swimming pool, it is essential to rinse off to maintain water quality and guarantee the safety of all swimmers. Not rinsing off before swimming can lead to chemical reactions in the pool and the presence of harmful substances.
To make sure a clean and safe swimming environment, here are some reasons why rinsing off is necessary:
- Over 70% of people do not rinse off before swimming.
- Chlorine cannot eliminate all harmful substances in water.
- Rinsing off before swimming helps prevent chemical reactions in the pool.
- Failure to rinse off can result in chemicals harmful to the human body.
Anyone Can Float With Proper Technique
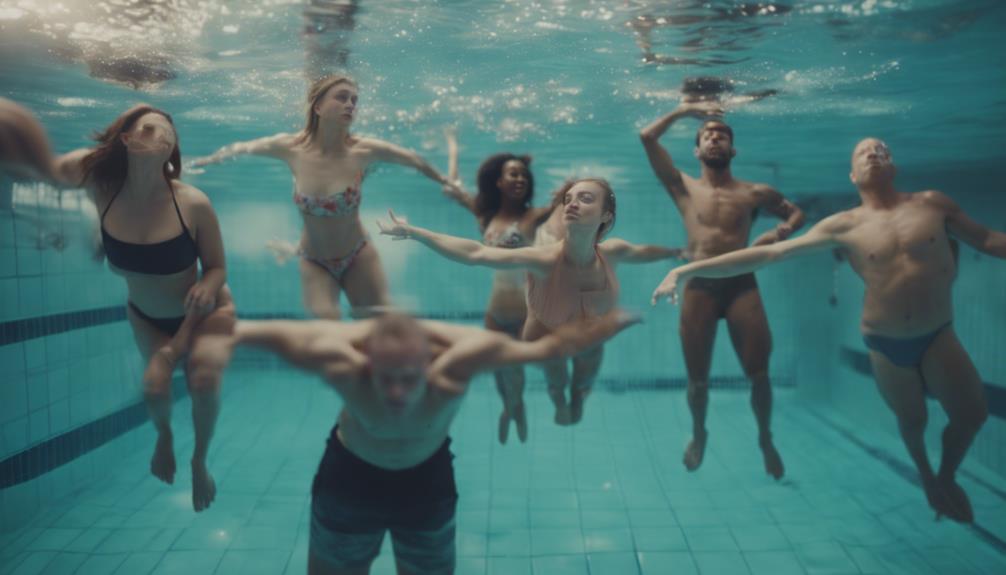
Is it possible for anyone to achieve buoyancy in water with proper technique and understanding of body composition?
While body type and genetic factors play a role in floating ability, with the right technique, almost anyone can float in water. Buoyancy is influenced by body fat percentage, bone density, muscle composition, and lung size.
By mastering relaxation techniques, controlling breathing, and distributing body weight evenly, individuals can improve their ability to float. Proper body positioning, such as lying flat with limbs spread out, helps increase buoyancy.
With practice and guidance on body awareness, even those who struggle initially can learn to float effortlessly in the water.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Swimming Right After Eating Really Cause Drowning?
Swimming immediately after eating does not cause drowning. Cramping from digestion may occur, but drowning is not a risk. While there is no set time limit, waiting a bit or opting for light snacks before swimming is advisable.
Is Sunscreen Necessary if I'm Swimming in a Pool?
Sunscreen is essential while swimming in a pool as water intensifies harmful UV rays. Submerging increases the risk of sunburn, doubling with water reflection. Use waterproof sunscreen with 30SPF or higher to prevent skin damage and reduce the risk of sunburn.
Will My Sunburn Eventually Turn Into a Tan?
Sunburned skin does not naturally turn into a tan. Instead, sunburn signifies skin damage from excessive UV exposure. Immediate treatment and sunscreen application are essential to prevent complications like sun poisoning and skin cancer.
Why Is Rinsing off Before Swimming so Important?
Rinsing off before swimming is essential as it helps remove dirt, sweat, and personal care products that can react with pool chemicals. This practice minimizes the formation of harmful compounds in the water, ensuring a safer swimming environment for all.
Can Everyone Float With the Right Technique?
Over 70% of people do not rinse off before swimming. Buoyancy varies due to body composition factors like fat distribution, muscle density, and lung size. While some may struggle, most individuals can float with the right technique and practice.
Conclusion
To wrap up, debunking prevalent myths surrounding summer swimming is crucial for promoting safety and enjoyment in the water.
One intriguing statistic to take into account is that based on the CDC, approximately 10 individuals pass away from accidental drowning daily in the United States.
By dispelling false information and offering precise details, we can assist in lessening the dangers linked with swimming and guarantee a more secure aquatic experience for everyone.









